JHU Engineering
Design Day
Experience the intersection of theory and practice as students unveil over 200 innovative solutions addressing real-world challenges at our engineering showcase event.
JHU Engineering Design Day
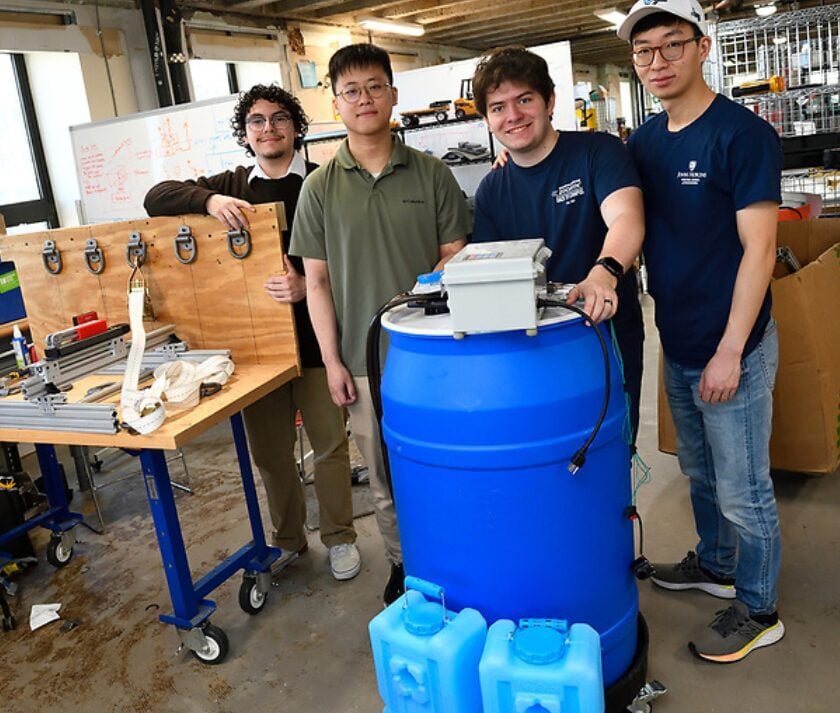
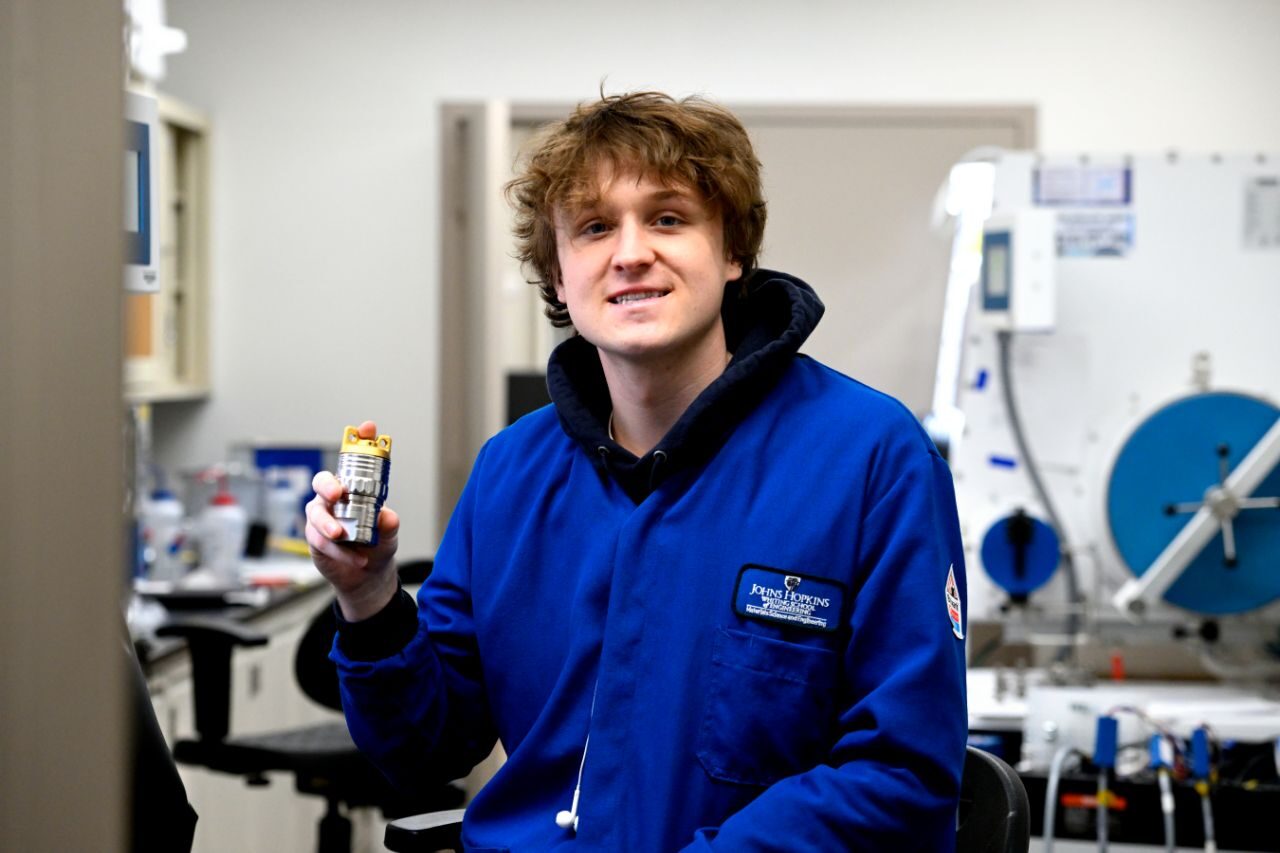
Johns Hopkins Engineering Design Day is the Whiting School’s premier event that showcases the innovative works of Hopkins engineering students. Come see how students implement their classroom knowledge, creativity, and problem-solving skills to develop inventions and processes that solve real-world problems and create a better future.
Congratulations to all on a fantastic 2025 event!
Information on JHU Engineering Design Day 2026 coming soon.
Schedule At-a-Glance
8:30 to 11:30 a.m. | Student Presentations
12 to 1:30 p.m. | Keynote Session and Lunch
1:30 to 3:30 p.m. | Poster Session
3:30 to 4 p.m. | Awards Presentation and Closing Remarks