People
| Postdoc | Lakshmana Chandrala, Omri Ram |
| Former Postdoc | David W. Murphy, Pranav R. Joshi |
| Graduate Student | Xinzhi Xue |
| Former Graduate Student | Kaushik Sampath, Cheng Li |
| Undergraduate Student | Anne Hosler, David Morra, Ben Chello, Yvana Ahdab, Kyle Candela |
| Project Supervisor | Prof. Joseph Katz |
| Design & Technical Support | Dr. Yury Ronzhes |
Aerosolization of Crude Oil-Dispersant slicks due to Bubble Bursting
Background
Breaking waves entrain air, resulting in the formation of subsurface bubbles. Aerosolization of crude oil slicks due to the bursting of these bubbles as they rise back to the ocean surface is one of the likely sources of oily marine aerosols. Application of chemical dispersants on oil slicks, which reduces the oil-water interfacial tension, alter the size distribution of the aerosols.
Objective
To characterize aerosol emission from an oil-contaminated surface due to bubble bursting.
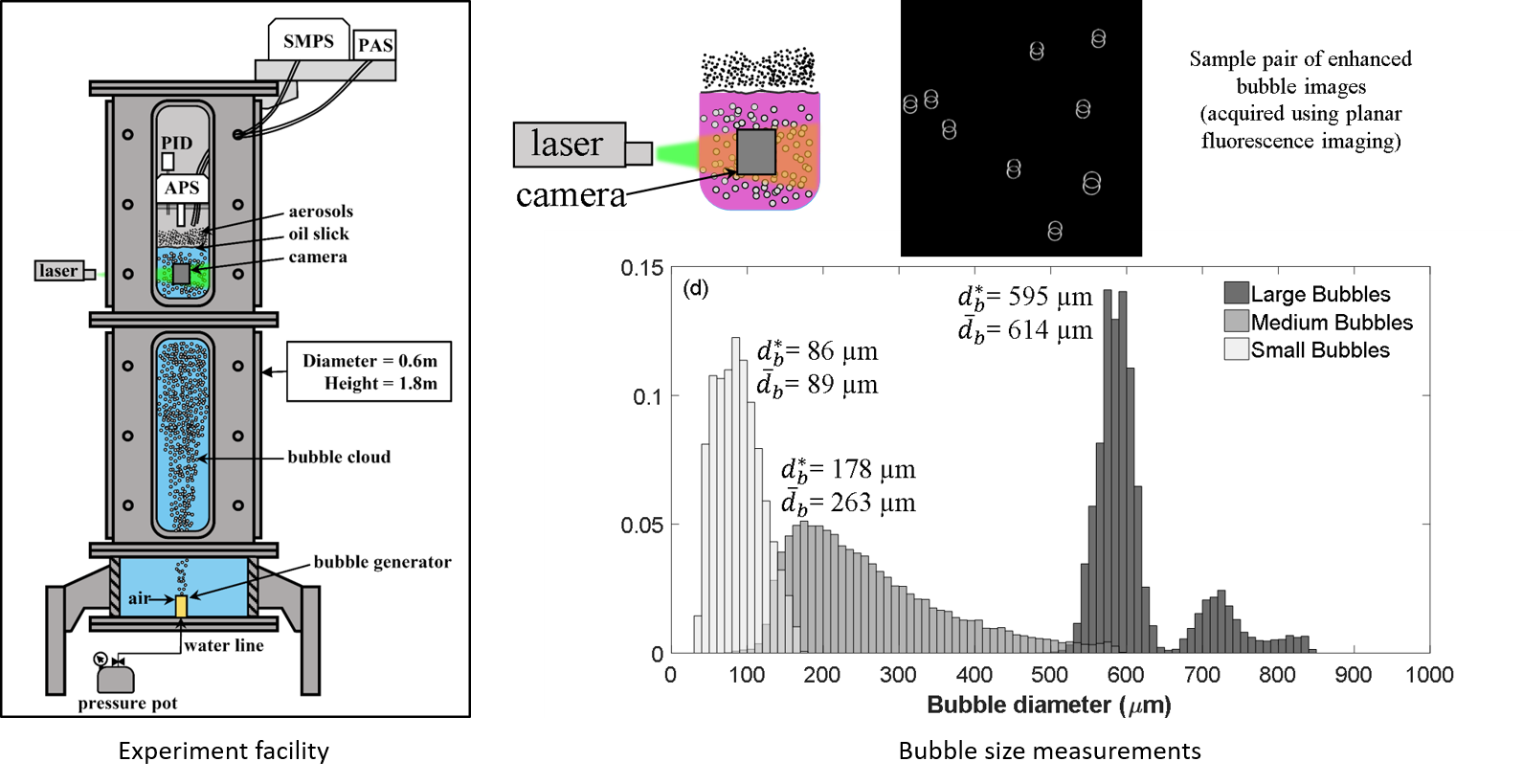 Facility
Facility
Bubble plumes with mode diameters of 86µm (small), 178 µm (medium) and 595 µm (large) are injected into a seawater column covered by slicks of crude oil, pure Corexit 9500A dispersant, and premixed dispersant and crude oil at a ratio (DOR) of 1:25. Size distribution of the sub-micron particles (10-370 nm), averaged over periods of 63-s, is measured using a scanning mobility particle sizer, SMPS model 3938 (TSI Inc.), with an electrostatic classifier model 3082 and a condensation particle counter model 3787.
Results
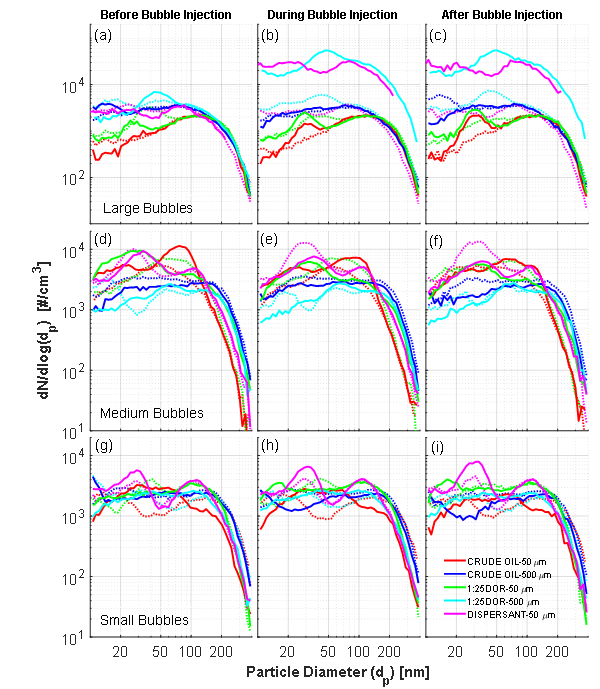
Sub-micron particle size distributions
Distributions of nano-sized particle number concentrations for the: (a, b, c) large,
(d, e, f) medium and (g, h, i) small bubble plumes in the exposed to laboratory air.
Results show that for the 500 µm thick slick of DOR-1:25 oil and 50 µm slick of pure dispersant exposed to ambient air, the large bubble plume causes an order of magnitude increase in the nano- (10-400 nm) droplet concentration.
Micron particle size distributions
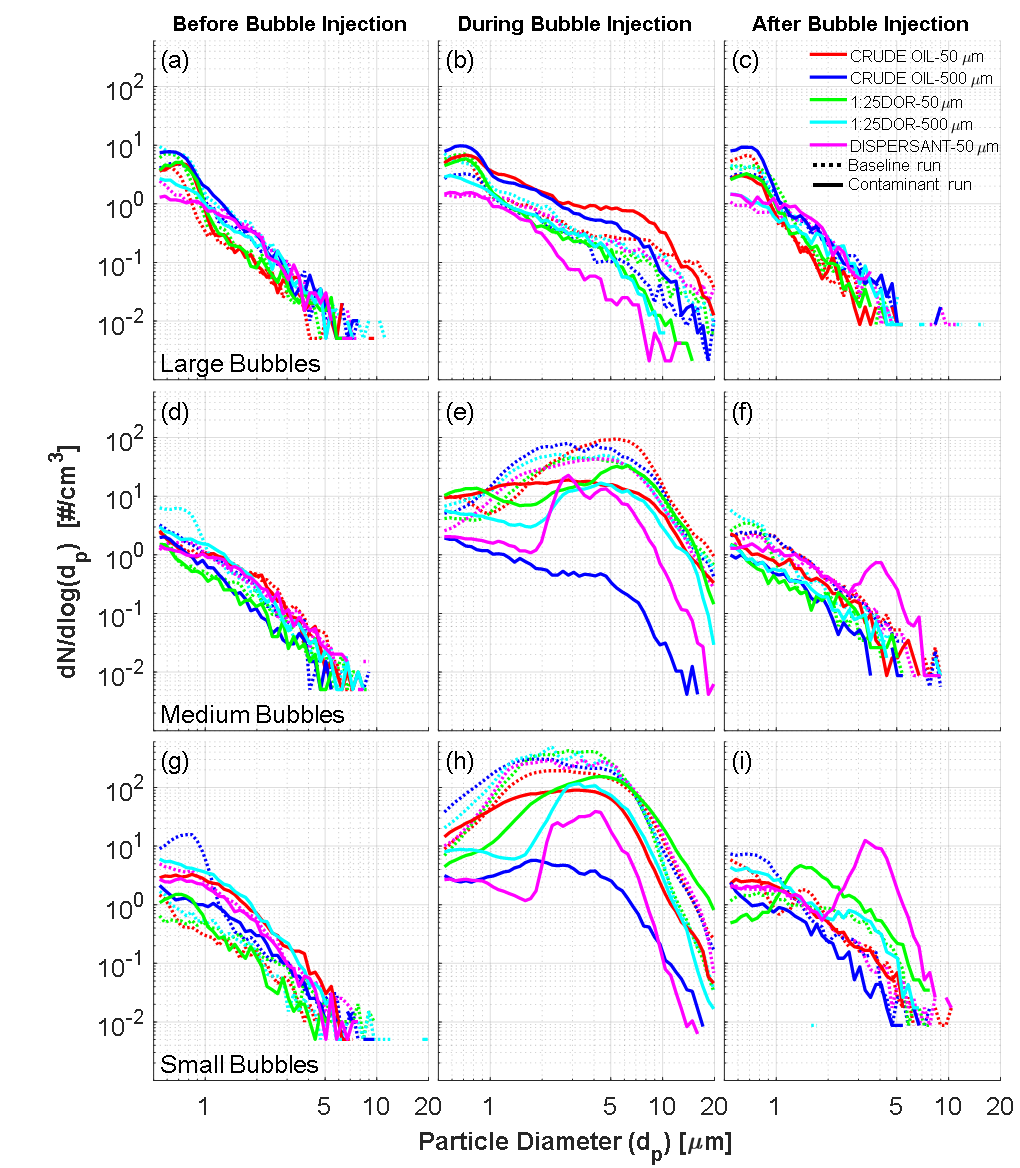 Distributions of micron-sized particle number concentrations for the (a, b, c)
Distributions of micron-sized particle number concentrations for the (a, b, c)
large, (d, e, f) medium and (g, h, i) small bubble plume.
For the same contaminant, the micro-droplet concentration decreases with increasing slick thickness. Particularly striking is a two orders of magnitude reduction in the micro-droplet concentration when 500 µm crude oil slicks are exposed to medium and small bubbles.
Summary
-
Bursting of bubbles in slicks containing crude oil and dispersant mixtures aerosolizes the oil, generating micro- and nano-droplets.
-
Resuspension of ambient nano-particles deposited on the water surface causes an order of magnitude increase in nano-aerosol concentration.
-
Micro-droplets are generated for all bubble plumes and slick types, but their concentration decreases with increasing slick thickness.
Publications
Chandrala, L. D., Afshar-Mohajer, N., Nishida, K., Ronzhes, Y., Sidhaye, V. K., Koehler, K., & Katz, J. (2019). A Device for measuring the in-situ response of Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells to airborne environmental agents. Scientific reports, 9(1), 1-12.
Sampath, N. A. Mohajer, L. Chandrala, W. Heo, J. Gilbert, D. Austin, K. Koehler, and J. Katz., (2019). Aerosolization of crude oil‐dispersant slicks due to bubble bursting. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 124(10), 5555-5578.
Li, C., Miller, J., Wang, J., Koley, S. S., & Katz, J. (2017). Size distribution and dispersion of droplets generated by impingement of breaking waves on oil slicks. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 122(10), 7938-7957.
Murphy, D. W., Xue, X., Sampath, K., & Katz, J. (2016). Crude oil jets in crossflow: effects of dispersant concentration on plume behavior. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 121(6), 4264-4281.
Murphy, D. W., Li, C., d’Albignac, V., Morra, D., & Katz, J. (2015). Splash behaviour and oily marine aerosol production by raindrops impacting oil slicks. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 780, 536-577.
Murphy, D., Morra, D., & Katz, J. (2013). Rain Drops and Oil Slicks: Impact of Water Droplets on a Surface Oil Layer. 66th Annual Meeting of the Division of Fluid Dynamics, Bulletin of the American Physical Society, 58.
Katz, J., Murphy, D., & Morra, D. (2013). Large Scale Behavior and Droplet Size Distributions in Crude Oil Jets and Plumes. 66th Annual Meeting of the Division of Fluid Dynamics, Bulletin of the American Physical Society, 58.
Li, C., Holser, A., & Katz, J. (2013). Breakup of an oil slick mixed with dispersants by breaking wave. 66th Annual Meeting of the Division of Fluid Dynamics, Bulletin of the American Physical Society, 58.